CHILD ABUSE
What Are the Types and Symptoms of Abuse?
Types of abuse can be listed as physical, emotional, and sexual abuse.
PHYSICAL ABUSE
It is the physical damage of the child without accident and the deterioration of his bodily integrity. Some examples of physical abuse include:
- Slap and punch, kick, throw
- Bite, hit, burn
- Damage with certain objects (knives, belts, etc.)
- Pulling hair and ears
How is physical abuse noticed?
Some symptoms:
- Unexplained, non-accidental injuries, bruises, impact marks, burns, fractures, and dislocations
- Physical complaining such as headaches, abdominal pain
- Clothes that do not comply with the seasonal conditions and are worn to hide the body
- School absence and/or low school success
- Failure to comply with school rules, disciplinary offenses
- Difficulty in regulating emotions and expressing oneself
- Difficulty in forming relationships (with peer, teacher, and family)
- Depressive (sad, unhappy, depressed) mood
- Suicidal thoughts
ATTENTION
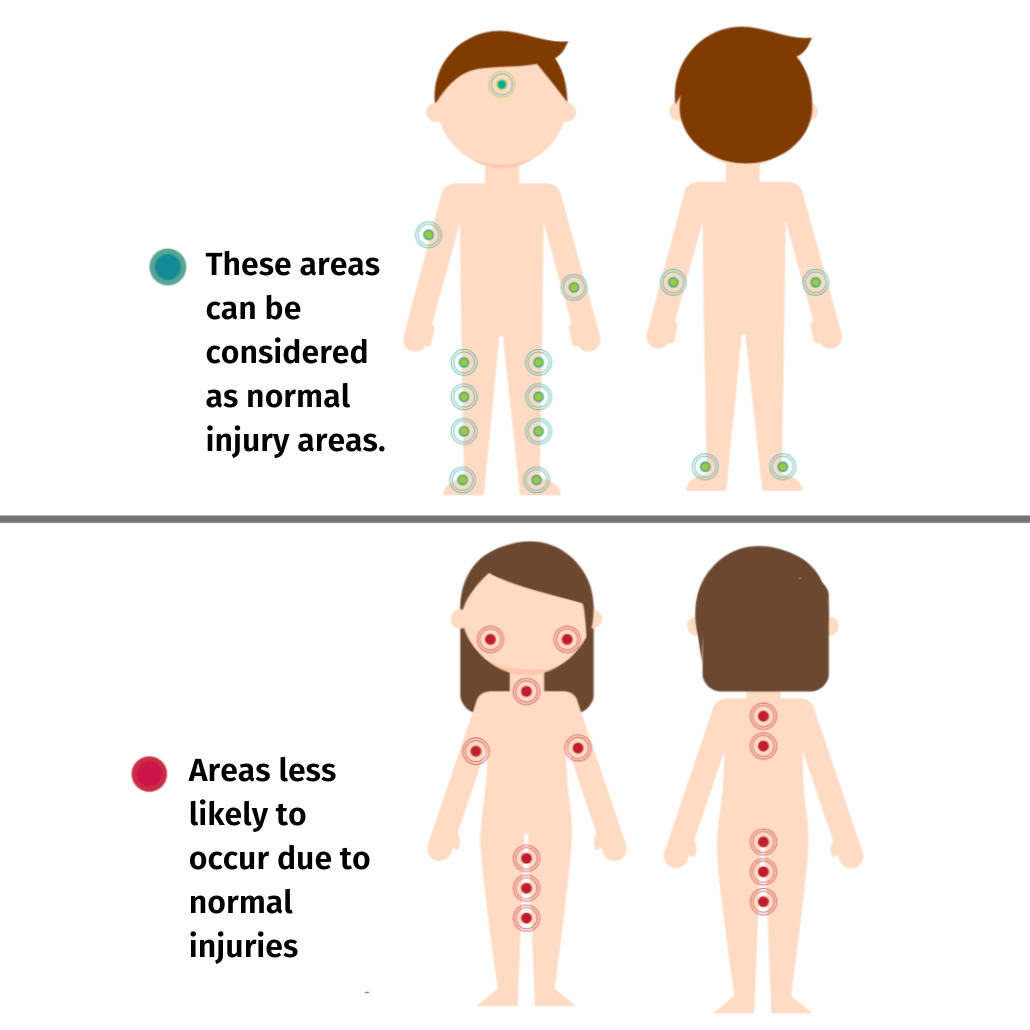
Abuse injury and accidental injury are different. To distinguish them, there are three basic points to consider:
- Frequency of injuries (If injuries occur frequently, there is a high probability of abuse injury.)
- Lack of a logical explanation for injuries
- In which part of the body the injuries are (Accidental injuries occur in bony parts of the body, while injuries caused by abuse occur in soft tissues)
EMOTIONAL ABUSE
The adolescent’s encounter with attitudes and behaviors that negatively affect him or her or the lack of care, love, and care he/she needs is a case of psychological harm according to social and scientific standards. It is all kinds of behaviors that harm the emotional integrity and personality development of the adolescent. Some examples of emotional abuse:
- Pretending it doesn’t exist emotionally (ignoring, neglecting, and violating)
- Not showing the love, care, and closeness it needs
- Not asking for your opinion, not caring or not caring
- Continuous criticism without any sign of support and guidance
- Humiliate, reject
- To blame, to punish
- Mocking, nicknamed
How to spot emotional abuse?
Some symptoms:
- Inadequate self-care
- Expulsion due to low academic achievement
- Low self-esteem
- Consistent passive (timid) or aggressive behavior
- Conflicts in peer relations
- Introversion
- Destructive behavior, including criminal offenses
- Suicidal thoughts
SEXUAL ABUSE
It is the use of the child by an adult or sexually mature adolescent for sexual stimulation and satisfaction. Sexual abuse can be in ways that involve contact and do not involve contact.
Examples of non-contact sexual abuse:
- Verbal abuse / sexually explicit speech (without paying attention to the impact it has on the other party)
- Exhibitionism
- Displaying pornographic material such as videos and photos to children/teenagers
- Taking or using sexually explicit photos/videos of a child/teenager for pornographic purposes
- Voyeurism
Examples of sexual abuse involving contact:
- Any behavior involving contact with sexual touch/intimate areas
- Sexual exploitation (pornography and prostitution)
- Aggression/rape
How is sexual abuse noticed?
Some symptoms:
- Difficulty walking or sitting
- Physical complaints (stomach ache and headache, vomiting)
- Pain, swelling, reddening, bleeding around the lips/mouth and genital/anal without explanation
- Need for excessive cleaning or neglect of cleanliness
- Excessively risky behaviors (self-harm) and suicide attempts
Well-Known Mistakes in Child Abuse
MISTAKE
If it doesn’t involve physical contact, it’s not abuse.
TRUE
Physical abuse involving contact is just one of the types of abuse. Abuse can be verbal, emotional, sexual, economic, and social.
MISTAKE
He/she’s lying, and if it were real, he/she’d explain what happened right after it happened.
TRUE
Abused children/adolescents may not be able to describe their abuse because they are ashamed, scared, feel unbelievable, or feel responsible for what happened. If the child comes to you and talks about a state of abuse, BELIEVE him/her. Kids don’t lie about that.
MISTAKE
Since it’s happened more than once, it’s not abuse, it’s consent.
TRUE
It does not imply consent that the victim of abuse does not tell what happened. There are many reasons why he/she won’t tell me what happened. He may have been threatened by his/her attacker, he/she may feel shame and guilt. Sometimes the victim can shut up because he/she’s afraid the family will fall apart.
MISTAKE
Only children from low-income families are abused.
TRUE
Children of all socioeconomic levels, any sociocultural group can be subjected to abuse.
MISTAKE
TRUE
Abusers are usually people with whom the child is in close contact and knows family, relatives.
MISTAKE
Only girls are at risk.
TRUE
Both boys and girls are at risk.